ASTM F1962-22
(Guide)Standard Guide for Use of Maxi-Horizontal Directional Drilling for Placement of Polyethylene Pipe or Conduit Under Obstacles, Including River Crossings
Standard Guide for Use of Maxi-Horizontal Directional Drilling for Placement of Polyethylene Pipe or Conduit Under Obstacles, Including River Crossings
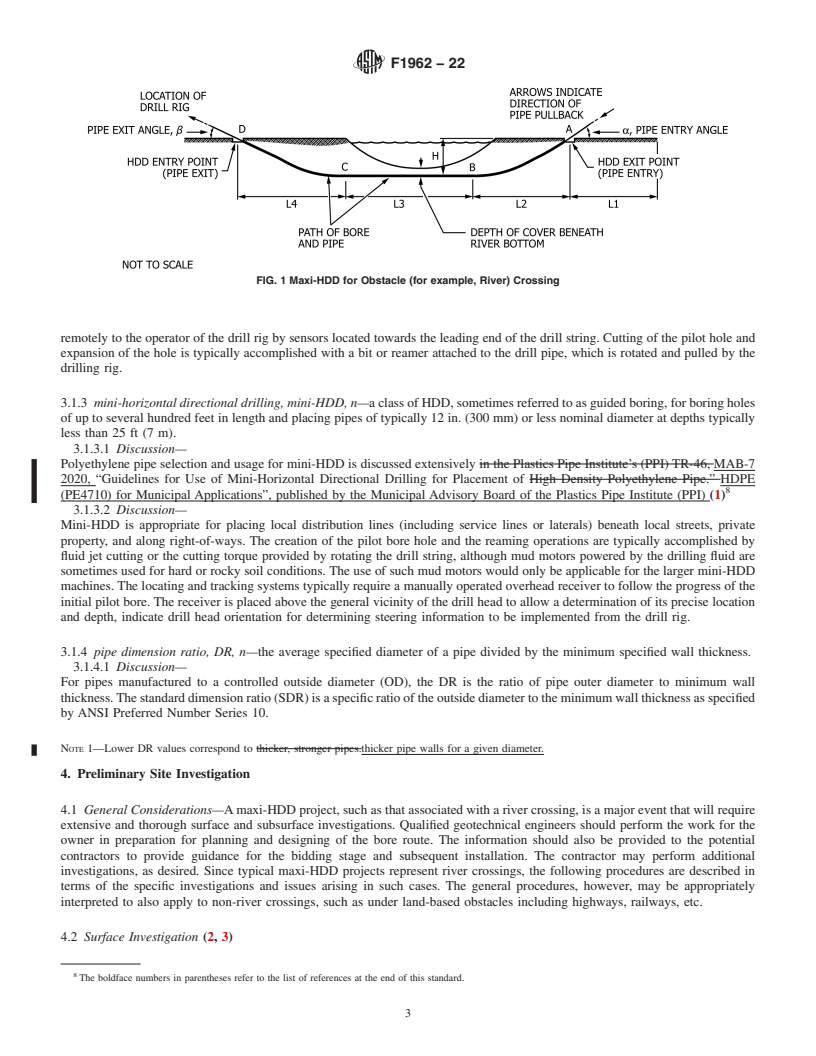
ABSTRACT
This guide describes the design, selection considerations, and installation procedures for the placement of polyethylene pipe or conduit below ground using maxi-horizontal directional drilling equipment. The pipes or conduits may be used for various applications including telecommunications, electric power, natural gas, petroleum, water lines, sewer lines, or other fluid transport. Horizontal directional drilling is a form of trenchless technology. The equipment and procedures are intended to minimize surface damage, restoration requirements, and disruption of vehicular or maritime traffic with little or no interruption of other existing lines or services. Mini-horizontal directional drilling (min-HDD) is typically used for the relatively shorter distances and smaller diameter pipes associated with local utility distribution lines. In comparison, maxihorizontal directional drilling (maxi-HDD) is typically used for longer distances and larger diameter pipes common in major river crossings. Applications that are intermediate to the mini-HDD or maxi-HDD categories may utilize appropriate “medi” equipment of intermediate size and capabilities. In such cases, the design guidelines and installation practices would follow those described for the mini- or maxi-HDD categories, as judged to be most suitable for each situation.
SCOPE
1.1 This guide describes the design, selection considerations, and installation procedures for the placement of polyethylene (PE) pipe or conduit below ground using maxi-horizontal directional drilling equipment. The pipes or conduits may be used for various applications including telecommunications, electric power, natural gas, petroleum, water lines, sewer lines, or other fluid transport.
1.2 Horizontal directional drilling is a form of trenchless technology. The equipment and procedures are intended to minimize surface damage, restoration requirements, and disruption of vehicular or maritime traffic with little or no interruption of other existing lines or services. Mini-horizontal directional drilling (mini-HDD) is typically used for the relatively shorter distances and smaller diameter pipes associated with local utility distribution lines. In comparison, maxi-horizontal directional drilling (maxi-HDD) is typically used for longer distances and larger diameter pipes common in major river crossings. Applications that are intermediate to the mini-HDD or maxi-HDD categories may utilize appropriate “medi” equipment of intermediate size and capabilities. In such cases, the design guidelines and installation practices would follow those described for the mini- or maxi-HDD categories, as judged to be most suitable for each situation.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use. Section 6 contains general safety information related to the use of maxi-horizontal directional drilling equipment.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
General Information
Relations
Buy Standard
Standards Content (Sample)
This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization established in the Decision on Principles for the
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
Designation: F1962 − 22
Standard Guide for
Use of Maxi-Horizontal Directional Drilling for Placement of
Polyethylene Pipe or Conduit Under Obstacles, Including
1
River Crossings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1962; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision.Anumber in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval.A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope* 1.5 This international standard was developed in accor-
dance with internationally recognized principles on standard-
1.1 This guide describes the design, selection
ization established in the Decision on Principles for the
considerations,andinstallationproceduresfortheplacementof
Development of International Standards, Guides and Recom-
polyethylene (PE) pipe or conduit below ground using maxi-
mendations issued by the World Trade Organization Technical
horizontaldirectionaldrillingequipment.Thepipesorconduits
Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
may be used for various applications including
telecommunications, electric power, natural gas, petroleum,
2. Referenced Documents
water lines, sewer lines, or other fluid transport.
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
1.2 Horizontal directional drilling is a form of trenchless
D420Guide for Site Characterization for Engineering De-
technology. The equipment and procedures are intended to
sign and Construction Purposes
minimize surface damage, restoration requirements, and dis-
D422Test Method for Particle-SizeAnalysis of Soils (With-
ruption of vehicular or maritime traffic with little or no
3
drawn 2016)
interruption of other existing lines or services. Mini-horizontal
D1586TestMethodforStandardPenetrationTest(SPT)and
directional drilling (mini-HDD) is typically used for the
Split-Barrel Sampling of Soils
relatively shorter distances and smaller diameter pipes associ-
D1587Practice for Thin-Walled Tube Sampling of Fine-
ated with local utility distribution lines. In comparison, maxi-
Grained Soils for Geotechnical Purposes
horizontaldirectionaldrilling(maxi-HDD)istypicallyusedfor
D2113Practice for Rock Core Drilling and Sampling of
longer distances and larger diameter pipes common in major
Rock for Site Exploration
river crossings. Applications that are intermediate to the
D2166Test Method for Unconfined Compressive Strength
mini-HDD or maxi-HDD categories may utilize appropriate
of Cohesive Soil
“medi”equipmentofintermediatesizeandcapabilities.Insuch
D2435Test Methods for One-Dimensional Consolidation
cases, the design guidelines and installation practices would
Properties of Soils Using Incremental Loading
follow those described for the mini- or maxi-HDD categories,
D2513Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Gas Pressure
as judged to be most suitable for each situation.
Pipe, Tubing, and Fittings
1.3 Thevaluesstatedininch-poundunitsaretoberegarded
D2850Test Method for Unconsolidated-Undrained Triaxial
as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
Compression Test on Cohesive Soils
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only
D3035SpecificationforPolyethylene(PE)PlasticPipe(DR-
and are not considered standard.
PR) Based on Controlled Outside Diameter
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the
D4186Test Method for One-Dimensional Consolidation
safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the Properties of Saturated Cohesive Soils Using Controlled-
responsibility of the user of this standard to establish appro-
Strain Loading
priate safety, health, and environmental practices and deter- D4220 Practices for Preserving and Transporting Soil
mine the applicability of regulatory limitations prior to use.
Samples
Section6containsgeneralsafetyinformationrelatedtotheuse
of maxi-horizontal directional drilling equipment.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction ofASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM
Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.67 on Trenchless Standards volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on
Plastic Pipeline Technology. the ASTM website.
3
Current edition approved Nov. 15, 2022. Published December 2022. Last The last approved version of this historical standard is referenced on
previous edition approved in 2020 as F1962–20. DOI: 10.1520/F1962-22. www.astm.org.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, P
...
This document is not an ASTM standard and is intended only to provide the user of an ASTM standard an indication of what changes have been made to the previous version. Because
it may not be technically possible to adequately depict all changes accurately, ASTM recommends that users consult prior editions as appropriate. In all cases only the current version
of the standard as published by ASTM is to be considered the official document.
Designation: F1962 − 20 F1962 − 22
Standard Guide for
Use of Maxi-Horizontal Directional Drilling for Placement of
Polyethylene Pipe or Conduit Under Obstacles, Including
1
River Crossings
This standard is issued under the fixed designation F1962; the number immediately following the designation indicates the year of
original adoption or, in the case of revision, the year of last revision. A number in parentheses indicates the year of last reapproval. A
superscript epsilon (´) indicates an editorial change since the last revision or reapproval.
1. Scope*
1.1 This guide describes the design, selection considerations, and installation procedures for the placement of polyethylene (PE)
pipe or conduit below ground using maxi-horizontal directional drilling equipment. The pipes or conduits may be used for various
applications including telecommunications, electric power, natural gas, petroleum, water lines, sewer lines, or other fluid transport.
1.2 Horizontal directional drilling is a form of trenchless technology. The equipment and procedures are intended to minimize
surface damage, restoration requirements, and disruption of vehicular or maritime traffic with little or no interruption of other
existing lines or services. Mini-horizontal directional drilling (min-HDD)(mini-HDD) is typically used for the relatively shorter
distances and smaller diameter pipes associated with local utility distribution lines. In comparison, maxi-horizontal directional
drilling (maxi-HDD) is typically used for longer distances and larger diameter pipes common in major river crossings. Applications
that are intermediate to the mini-HDD or maxi-HDD categories may utilize appropriate “medi” equipment of intermediate size and
capabilities. In such cases, the design guidelines and installation practices would follow those described for the mini- or maxi-HDD
categories, as judged to be most suitable for each situation.
1.3 The values stated in inch-pound units are to be regarded as standard. The values given in parentheses are mathematical
conversions to SI units that are provided for information only and are not considered standard.
1.4 This standard does not purport to address all of the safety concerns, if any, associated with its use. It is the responsibility
of the user of this standard to establish appropriate safety, health, and environmental practices and determine the applicability of
regulatory limitations prior to use. Section 6 contains general safety information related to the use of maxi-horizontal directional
drilling equipment.
1.5 This international standard was developed in accordance with internationally recognized principles on standardization
established in the Decision on Principles for the Development of International Standards, Guides and Recommendations issued
by the World Trade Organization Technical Barriers to Trade (TBT) Committee.
2. Referenced Documents
2
2.1 ASTM Standards:
D420 Guide for Site Characterization for Engineering Design and Construction Purposes
1
This guide is under the jurisdiction of ASTM Committee F17 on Plastic Piping Systems and is the direct responsibility of Subcommittee F17.67 on Trenchless Plastic
Pipeline Technology.
Current edition approved Nov. 1, 2020Nov. 15, 2022. Published November 2020December 2022. Last previous edition approved in 20112020 as F1962–11 which was
withdrawn July 2020 and reinstated in November 2020. DOI: 10.1520/F1962-11.–20. DOI: 10.1520/F1962-22.
2
For referenced ASTM standards, visit the ASTM website, www.astm.org, or contact ASTM Customer Service at service@astm.org. For Annual Book of ASTM Standards
volume information, refer to the standard’s Document Summary page on the ASTM website.
*A Summary of Changes section appears at the end of this standard
Copyright © ASTM International, 100 Barr Harbor Drive, PO Box C700, West Conshohocken, PA 19428-2959. United States
1
---------------------- Page: 1 ----------------------
F1962 − 22
3
D422 Test Method for Particle-Size Analysis of Soils (Withdrawn 2016)
D1586 Test Method for Standard Penetration Test (SPT) and Split-Barrel Sampling of Soils
D1587 Practice for Thin-Walled Tube Sampling of Fine-Grained Soils for Geotechnical Purposes
D2113 Practice for Rock Core Drilling and Sampling of Rock for Site Exploration
D2166 Test Method for Unconfined Compressive Strength of Cohesive Soil
D2435 Test Methods for One-Dimensional Consolidation Properties of Soils Using Incremental Loading
3
D2447 Specification for Polyethylene (PE) Plastic Pipe, Schedules 40 and 80, Based on Outside Dia
...










Questions, Comments and Discussion
Ask us and Technical Secretary will try to provide an answer. You can facilitate discussion about the standard in here.